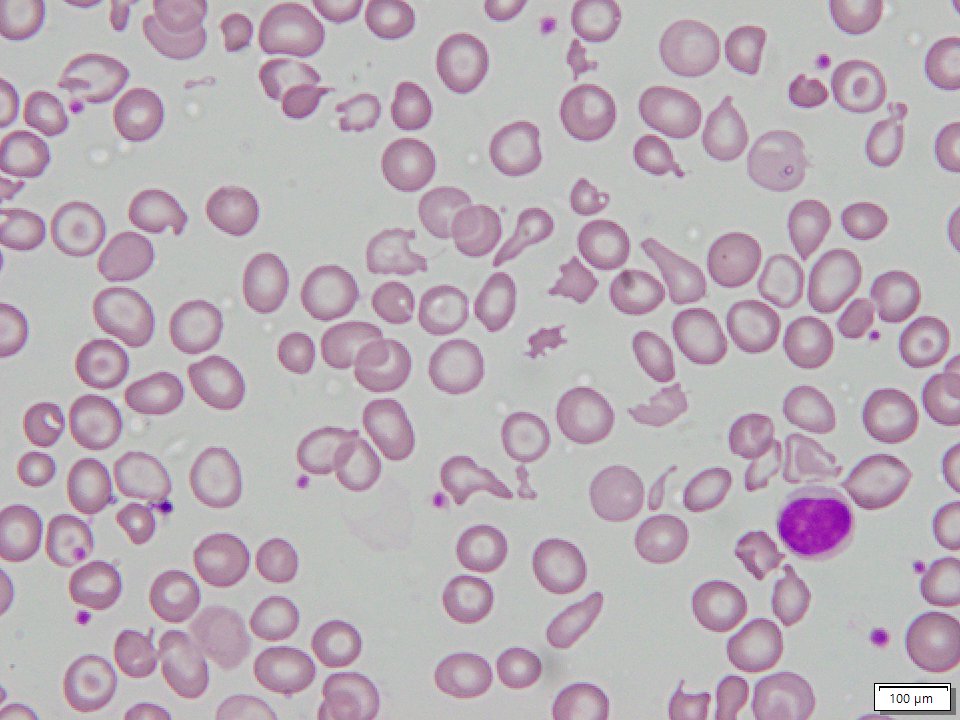
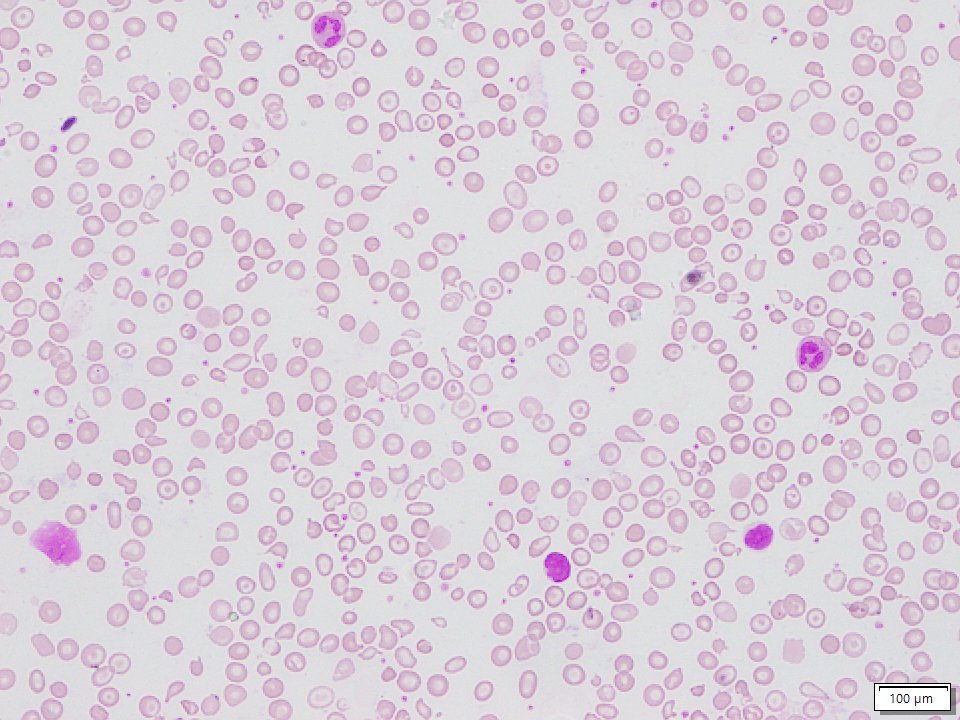
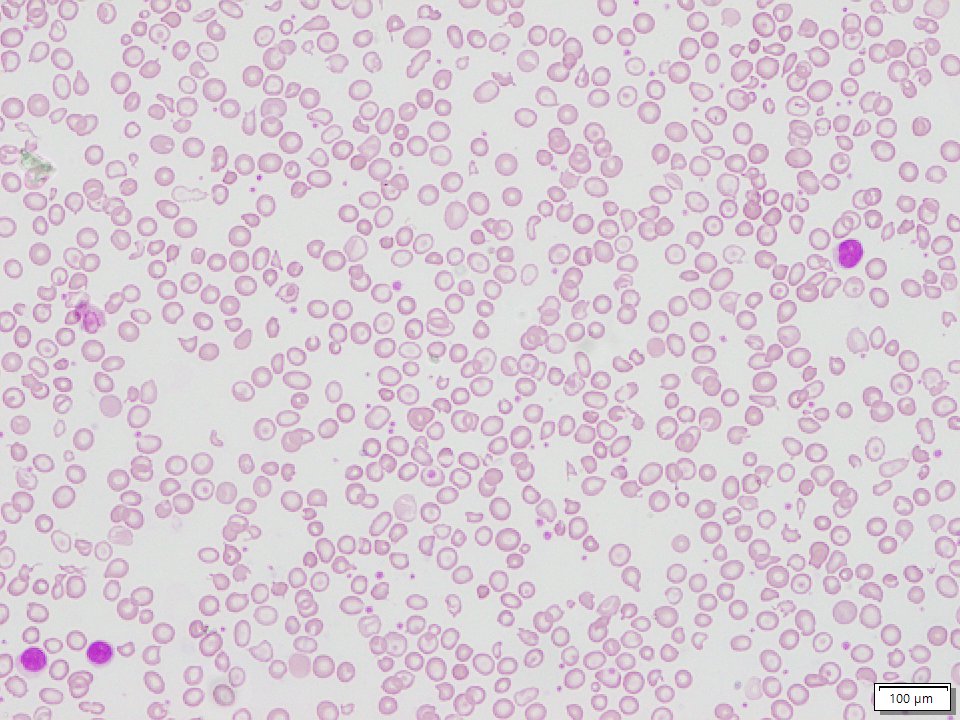
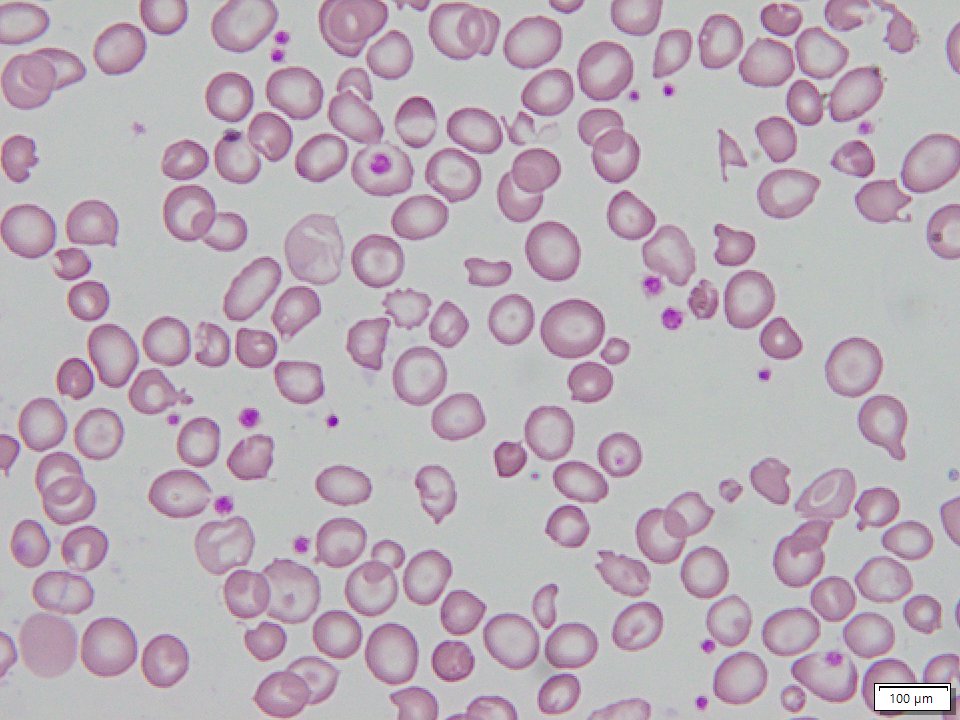
Beta Thalassemia Major
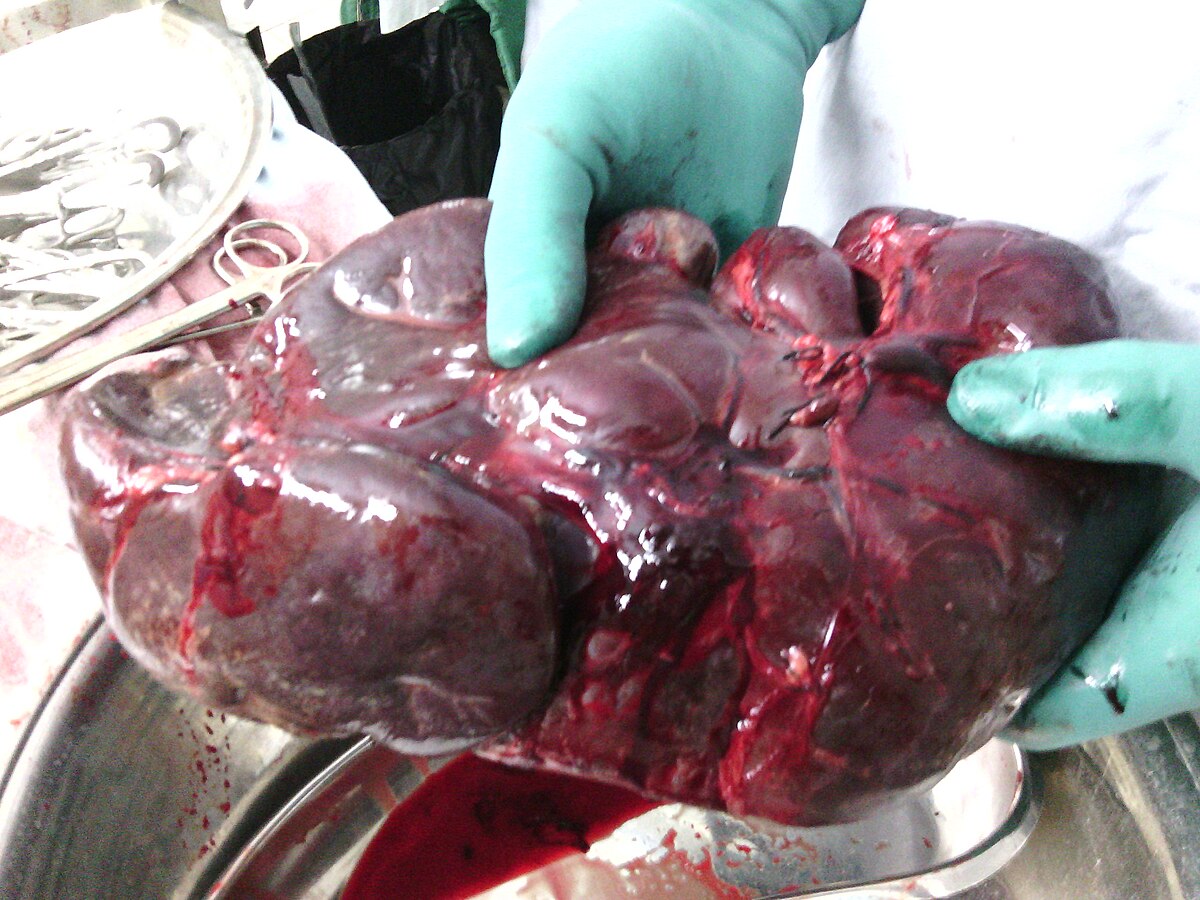
Surgically removed spleen of a Thalassemic child. It is about 15 times larger than normal.
Affected children require regular lifelong blood transfusions. Bone marrow transplants can be curative for some children.[34] Patients receive frequent blood transfusions that lead to or potentiate iron overload.[35] Iron chelation treatment is necessary to prevent damage to internal organs in cases of iron overload. Advances in iron chelation treatments allow patients with thalassemia major to live long lives with access to proper treatment. Popular chelators include deferoxamine and deferiprone.[36][37]
The oral chelator deferasirox was approved for use in 2005 in some countries,[38][39]. Bone marrow transplantation is the only cure and is indicated for patients with severe thalassemia major. Transplantation can eliminate a patient’s dependence on transfusions. Absent a matching donor, a savior sibling can be conceived by preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) to be free of the disease as well as to match the recipient’s human leukocyte antigen (HLA) type.[40]
Serum ferritin (the storage form of iron) is routinely measured in those with beta thalassemia to determine the degree of iron overload; with increased ferritin levels directing the use of iron chelation therapy. The three iron chelators; subcutaneous deferoxamine, oral deferiprone and oral deferasirox can be used as monotherapy or in combination, they have all been shown to decrease serum/systemic iron levels, hepatic and cardiac iron levels as well as decreasing the risk of cardiac arrhythmia, heart failure and death.[9] Hepatic and myocardial MRI is also used to quantify the iron deposition in target organs, especially the heart and liver, to guide therapy.[9]
Scientists at Weill Cornell Medical College have developed a gene therapy strategy that could feasibly treat both beta-thalassemia and sickle cell disease. The technology is based on delivery of a lentiviral vector carrying both the human β-globin gene and an ankyrin insulator to improve gene transcription and translation, and boost levels of β-globin production.[41